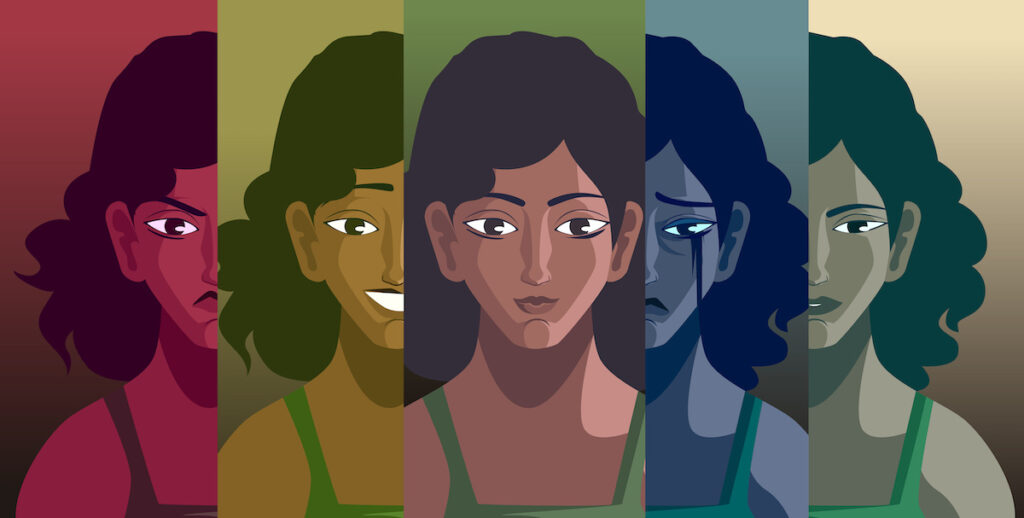
Borderline Personality Disorder (BPD) is a mental health disorder that affects how a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with BPD often experience intense and unstable emotions, have difficulties with relationships, and struggle with a sense of self-identity. BPD is a serious and complex disorder that can cause significant distress to the individual and those around them.
Here are some of the symptoms of Borderline Personality Disorder.
- Intense and Unstable Emotions: People with BPD often experience intense and rapid changes in their emotions, which can be triggered by minor events. They may feel intense anger, sadness, or anxiety, which can lead to impulsive behaviors like self-harm, substance abuse, or suicidal thoughts.
- Unstable Relationships: People with BPD often have difficulties with relationships, including fear of abandonment, idealization of others, and intense anger or disappointment when relationships do not meet their expectations. They may also struggle with maintaining boundaries or having a stable sense of self-identity within a relationship.
- Distorted Self-Image: People with BPD may have an unstable sense of self-identity, which can lead to feelings of emptiness or a lack of a clear sense of purpose. They may also have extreme and rapidly changing opinions about themselves, including feelings of worthlessness or grandiosity.
- Impulsive Behaviors: People with BPD may engage in impulsive behaviors, including substance abuse, reckless driving, binge eating, and compulsive shopping. These behaviors can be dangerous and lead to negative consequences, including legal issues or financial problems.
- Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors: People with BPD are at an increased risk for suicidal thoughts and behaviors. They may feel overwhelmed by their emotions and struggle with feelings of hopelessness and despair.
- Dissociation: People with BPD may experience episodes of dissociation, where they feel disconnected from their thoughts, feelings, and surroundings. This can lead to a sense of unreality or a feeling of being detached from oneself.
It is important to note that not everyone with BPD will experience all of these symptoms, and some may experience them to varying degrees. It is also important to seek professional help if you or someone you know is experiencing these symptoms. Treatment for BPD often includes therapy, medication, and support from loved ones. With proper treatment and support, people with BPD can lead fulfilling lives and manage their symptoms effectively.