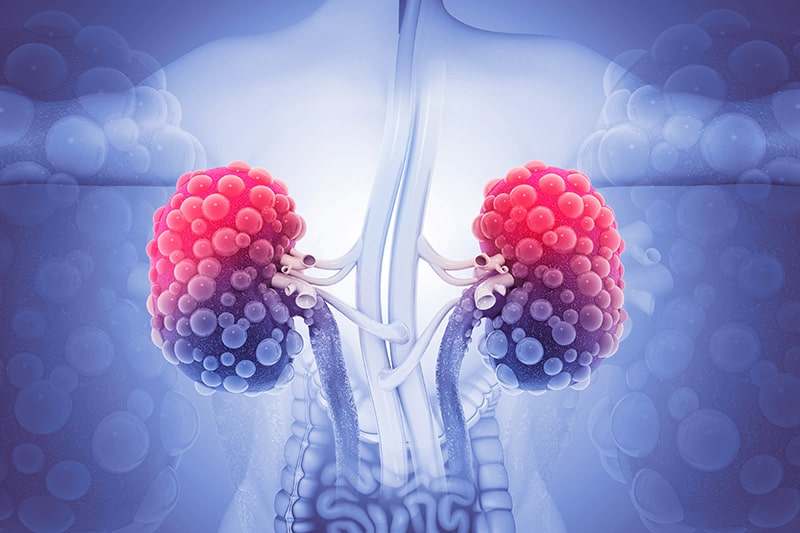
Nephropathy, also known as diabetic kidney disease, is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to kidney failure. Diabetes is the leading cause of kidney failure, accounting for 44% of new cases.
The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products from the blood and regulating the balance of fluids in the body. In people with diabetes, high levels of blood sugar can damage the small blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to nephropathy. This damage can cause the kidneys to lose their ability to filter waste effectively, which can lead to a build-up of toxins in the blood.
The early stages of nephropathy may have no symptoms, but as the disease progresses, it can lead to several serious complications, including:
- High blood pressure: Nephropathy can cause an increase in blood pressure, which can further damage the kidneys and increase the risk of heart disease and stroke.
- Anemia: As the kidneys lose their ability to produce erythropoietin, a hormone that stimulates the production of red blood cells, people with nephropathy may develop anemia.
- Fluid retention: When the kidneys are not functioning properly, fluid can build up in the body, causing swelling in the feet, ankles, and legs.
If left untreated, nephropathy can eventually lead to kidney failure, which requires dialysis or a kidney transplant to sustain life.
There are several ways to prevent or slow the progression of nephropathy:
- Tight control of blood sugar levels: Maintaining good blood sugar control can slow the progression of nephropathy and help prevent complications.
- Blood pressure control: Keeping blood pressure under control is important for preventing further damage to the kidneys.
- Regular kidney function tests: It is important to have regular check-ups with your doctor to monitor kidney function.
- Medications: Some medications may be prescribed to help slow the progression of nephropathy, such as ACE inhibitors or ARBs..
It is important to be aware of the potential complications of diabetes, including nephropathy, and to take steps to prevent or manage them. By working closely with your healthcare team and making lifestyle changes, you can reduce your risk of developing nephropathy and improve your overall health.
In conclusion, Nephropathy is a serious complication of diabetes that can lead to kidney failure. It is important to be aware of the potential complications of diabetes, including nephropathy, and to take steps to prevent or manage them, such as maintaining good blood sugar and blood pressure control, having regular kidney function tests and taking medications as prescribed by the doctor.